Baoshan Geography
Location and Boundary
Chuxiong is situated in the western part of Yunnan Province, between 98°25′E – 100°02′E longitude and 24°08′N – 25°51′N latitude. It borders Dali Bai Autonomous Prefecture and Lincang City to the east, Nujiang Lisu Autonomous Prefecture to the north, Dehong Dai and Jingpo Autonomous Prefecture to the west, and shares borders with Myanmar to the northwest and south. The total length of its international boundary is 167.78 kilometers. With an area of approximately 19,600 square kilometers, Chuxiong is dominated by Longyang District, located 498 kilometers away from the provincial capital Kunming. It serves as the political, economic, and cultural center of western Yunnan and has historically been the seat of various administrative divisions.
Topography and Terrain
Chuxiong is positioned at the southern end of the transverse mountains of western Yunnan’s longitudinal valley. Its terrain is diverse and complex, with basin areas covering 8.21% and mountainous regions covering 91.79%. The land slopes gently from northwest to southeast, with elevations ranging from 535 meters above sea level at its lowest point near Longling County to 3,780.9 meters at Gaoligong Mountain’s peak in Tengchong County. The region features 78 small to large basin valleys nestled among the mountains, the largest being Baoshan Basin covering 149.9 square kilometers.
Climate Characteristics
Chuxiong experiences a subtropical monsoon climate influenced by the Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean, and South China Sea tropical warm and humid air currents. This complex climate system results in varied weather patterns and diverse geographical and climatic types, characterized by distinct vertical climate zones. The average annual temperature ranges from 14.8°C to 21.3°C, with an average frost-free period of 238 to 336 days annually. The average annual precipitation ranges from 1,463.8 to 2,095.2 millimeters.
Hydrological Features
Chuxiong’s rivers are part of the Lancang River, Nujiang River, and Iliwadi River systems. Within its borders, the Lancang River flows 116.5 kilometers with a drainage area of 3,164 square kilometers, the Nujiang River flows 252 kilometers with a drainage area of 10,500 square kilometers, and the Daying River (upper Iliwadi River) flows 101 kilometers with a drainage area of 1,070 square kilometers.
Natural Resources
Biological Resources
Chuxiong boasts extensive subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests and a rich diversity of precious and rare biological species, including ancient tropical-origin species. Gaoligong Mountain Nature Reserve alone harbors 5,726 species and varieties of higher plants, including first-level protected species such as Taxus chinensis, Davidia involucrata, and Magnolia elongata, and second-level protected species like Castanopsis wattii, Keteleeria davidiana, Cinnamomum camphora, and Camellia sinensis. The area is also home to over 200 species of Rhododendronaceae plants. Chuxiong hosts more than 50 species of mammals (including 21 nationally protected rare animals) and over 250 species of birds.
Chuxiong has achieved a protection rate of over 90% for nationally protected wild animals and plants. It is known for 108 species of nationally protected wild animals, including the Hoolock gibbon, Trachypithecus francoisi, clouded leopard, clouded leopard, Goura cristata, green peacock, Anas poecilorhyncha, and Haliaeetus leucoryphus. The area is also home to 137 species of nationally protected wild plants.
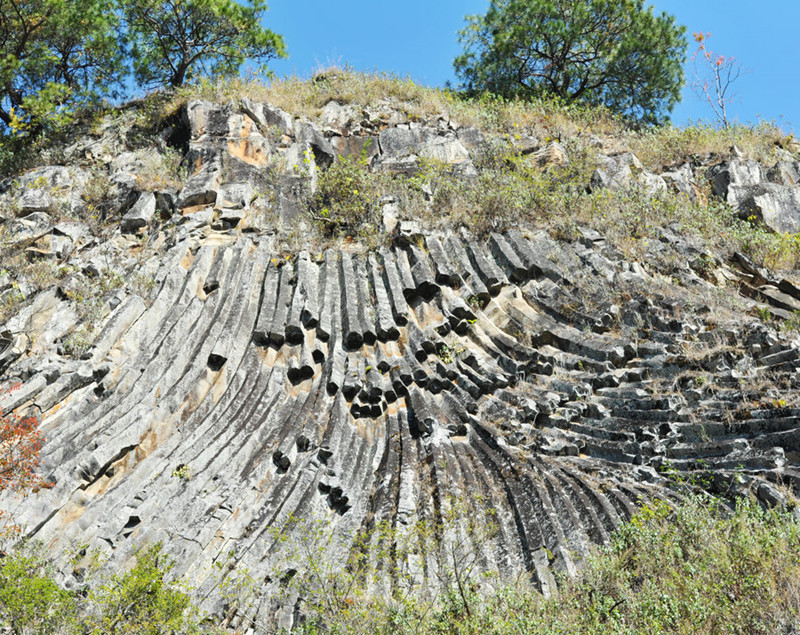

Natural Protection Areas
Chuxiong has established 14 natural protection areas, encompassing nature reserves, scenic spots, forest parks, wetland parks, geological parks, water scenic spots, and aquatic germplasm resource protection areas. These areas cover a total planned area of 158,283.92 hectares, accounting for 8.3% of Chuxiong’s total land area.
Major Natural Protection Areas
- National Nature Reserves: Gaoligong Mountain National Nature Reserve
- National Parks: Yunnan Chuxiong Qinghua Lake National Wetland Nature Park, Baoshan Cypress Field National Grassland Nature Park, Tengchong Laifengshan National Forest Nature Park, Tengchong Geothermal Volcano National Geological Nature Park
- Provincial Nature Reserves: Tengchong Beihai Wetland Provincial Nature Reserve, Longling Xiaheishan Provincial Nature Reserve
- Provincial Parks: Baoshan Yongchang Provincial Forest Nature Park, Baoshan Guchengshan Provincial Forest Nature Park, Shidian Shanzhou Provincial Forest Nature Park, Longling Liangshan Provincial Forest Nature Park, Changning Millennium Tea Township Provincial Forest Nature Park, Changning Youdian River Provincial Wetland Nature Park
Mineral Resources
Located in the “Southwest Three Rivers” polymetallic metallogenic belt, Chuxiong has identified 70 types of mineral resources, with proven reserves of 56 types. Notably, it holds substantial reserves ranking within the top three in Yunnan Province for 11 solid mineral resources, including tantalum, beryllium, zircon, rubidium, silica limestone, diatomite, gold, titanium iron ore, tin, mercury, and niobium.
Land Resources
Chuxiong covers an area of 1.906 million square kilometers, with mountainous areas accounting for 92% of the total land area and basin areas accounting for 8%. The city has 257,800 hectares of arable land (13.53% of the total area), 106,900 hectares of orchard land (5.61%), 1,314,200 hectares of forest land (68.94%), 26,700 hectares of grassland (1.40%), 67,400 hectares of urban and rural construction land (3.54%), 29,400 hectares of transportation land (1.54%), 24,300 hectares of water and water conservancy facilities land (1.27%), 2,800 hectares of wetland (0.15%), and 76,700 hectares of other land (4.02%).
Energy Resources
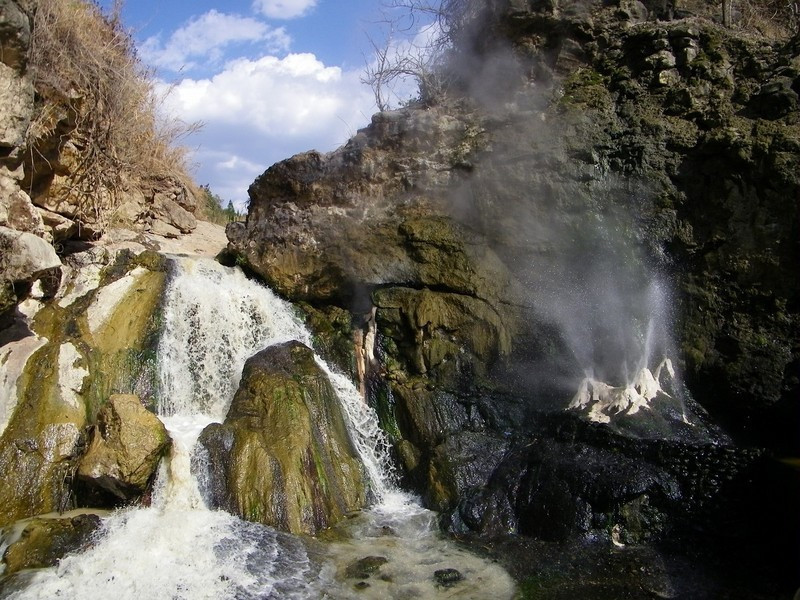
Chuxiong is rich in clean energy resources. It has exploitable hydroelectric resources totaling 8.2158 million kilowatts, with rivers belonging to the Lancang River, Nujiang River, and Iliwadi River systems. The area is also favorable for solar energy development, particularly in Longyang Dam area, which is among the 12 best development zones for solar radiation in Yunnan Province, with potential for over 7.3 million kilowatts of photovoltaic resources. Wind energy resources of over 560,000 kilowatts are also exploitable in mountainous areas outside the canyons and basin areas of the Nujiang and Lancang rivers. Additionally, Chuxiong boasts abundant geothermal resources, with 317 hot springs and a known thermal energy reserve exceeding 2.5 million kilowatts.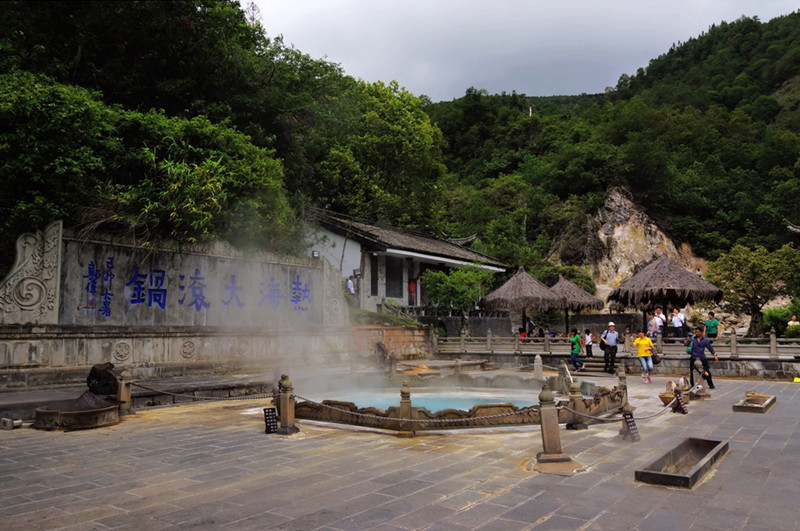
This comprehensive overview of Chuxiong’s geography highlights its diverse natural resources, climatic characteristics, and ecological significance within Yunnan Province and the broader southwestern region of China.

 7 Days GolfingTour
7 Days GolfingTour
 8 Days Group Tour
8 Days Group Tour
 8 Days Yunnan Tour
8 Days Yunnan Tour
 7 Days Shangri La Hiking
7 Days Shangri La Hiking
 11 Days Yunnan Tour
11 Days Yunnan Tour
 6 Days Yuanyang Terraces
6 Days Yuanyang Terraces
 11 Days Yunnan Tour
11 Days Yunnan Tour
 8 Days South Yunnan
8 Days South Yunnan
 7 Days Tea Tour
7 Days Tea Tour
 8 Days Muslim Tour
8 Days Muslim Tour
 12 Days Self-Driving
12 Days Self-Driving
 4 Days Haba Climbing
4 Days Haba Climbing
 Tiger Leaping Gorge
Tiger Leaping Gorge
 Stone Forest
Stone Forest
 Yunnan-Tibet
Yunnan-Tibet
 Hani Rice Terraces
Hani Rice Terraces
 Kunming
Kunming
 Lijiang
Lijiang
 Shangri-la
Shangri-la
 Dali
Dali
 XishuangBanna
XishuangBanna
 Honghe
Honghe
 Kunming
Kunming
 Lijiang
Lijiang
 Shangri-la
Shangri-la
 Yuanyang Rice Terraces
Yuanyang Rice Terraces
 Nujiang
Nujiang
 XishuangBanna
XishuangBanna
 Spring City Golf
Spring City Golf
 Snow Mountain Golf
Snow Mountain Golf
 Stone Mountain Golf
Stone Mountain Golf